As States are in lock-down and enforcing social distancing measures to continue avoiding a massive health crisis, this voluntary recession is unprecedented. However, while U.S. unemployment benefit claims have surged to 33 million in recent weeks, the majority of those filing claims are flagged as temporary unemployment, suggesting U.S. workers will get hired back once business loans or grants flow and state lockdowns ease.
Thankfully across most regions, including California—the nation’s most populous state—infection curves are starting to flatten. This brings hope that life outside our homes can start to resume. But absent a vaccine, extensive testing and coordinated efforts to re-open states in an orderly manner, social distancing will need to continue.
Returning to work won’t be a simultaneous grand opening. A staged reengagement is more likely and the ramp up won’t be uniform across U.S. states and professions. What does that mean for a recovery in the U.S. economy?
When Will Workers and Consumers Leave Their Homes?
A state-by-state analysis from the University of Washington's Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) recently indicated that “as early as May 4, some states may be able to relax some aspects of social distancing measures so long as ‘robust containment strategies’ are implemented to prevent a second wave of infections” but advises that actual decisions to relax social distancing should be informed by meeting critical metrics, including infection rates as low as 1 estimated infection per 1 million people.
Reengaging U.S. GDP
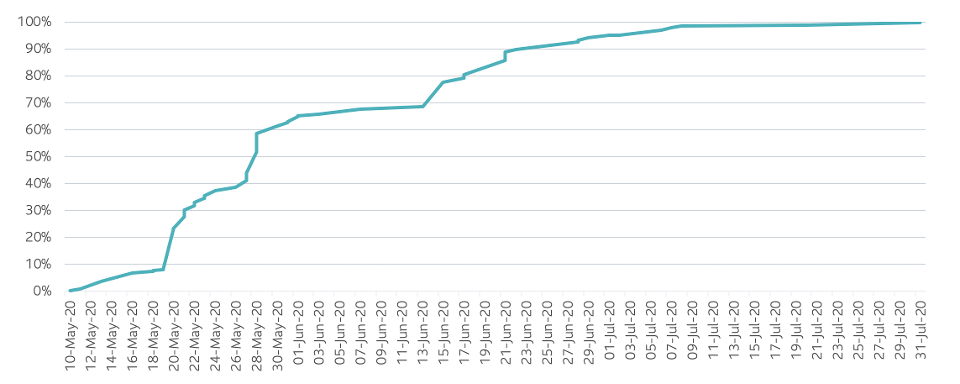
Source: IHME, US State level GDP
Reengaging US GDP SLC MANAGEMENT
At those levels, IHME modeling shows 28 states could start allowing people to get back to work, while others such as South Dakota, Nebraska, Utah, Arkansas and Oklahoma, may need to wait until late June or early July. For perspective, weighing those start dates by previous annual GDP suggests that two-thirds of potential output could be in startup phase by the end of May with the rest coming in during the course of the next two months.
However, while some “lights may be on”, staging a recovery will be an arduous path and will depend on how quickly companies can engage their full work force without risking a resurgence in COVID-19 cases.
Social Distancing in High-Contact Professions
Not all professions and industries carry the same risk of contagion by social interaction. Keeping staff six feet apart from their customers at high volume restaurants is much harder than between scientists at a research lab.
Research from the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis gives perspective on the distribution of jobs according to their level of face-to-face interaction. Its analysis combines data from the 2017 American Community Survey and an indicator of physical interaction developed by the Department of Labor with help from 0*Net.
High contact-intensity occupations include hairstylists and therapists, low contact include designers and scientists. Each profession is assigned a proximity score ranging from zero to 100 based on how close they interact with other people.
Professions within touching-distance score 100. A shared office, around 50. Work from home, zero. Close to 27% of the working population is low contact, while 22% is high, with 51% in the middle.
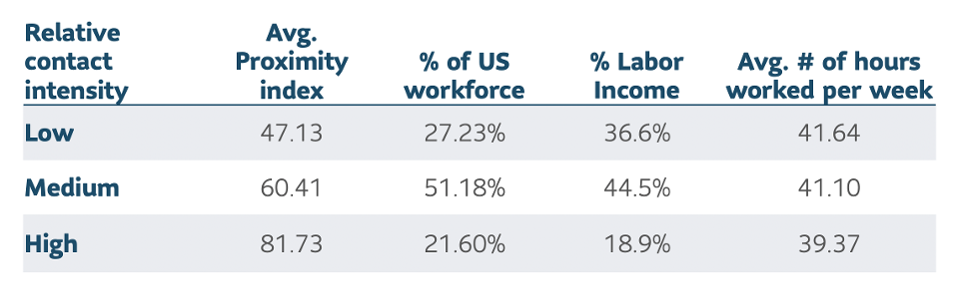
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of Saint Louis (Social Distancing and Contact-Intensive Occupations by F Leibovici, Ana Maria Santacreu, Matthew Famiglietti, March 2020). Using data from American Community Survey, 0*Net.
Relative contact intensity SLC MANAGEMENT
And across most U.S. states, the dependence on high contact professions ranges from 20 to 25%. Given how important these professions are to most states’ economic activity, the need to get extensive testing in place is ever more urgent, as these workers are more susceptible and active conduits.
U.S States: Share of workers in high contact-intensive occupations
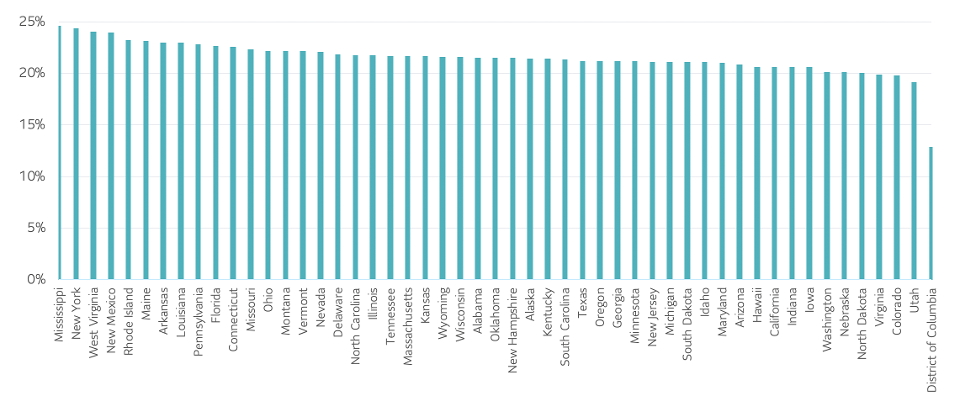
Source: American Community Survey, 0*Net
US States: Share of workers in high contact intensive occupations SLC MANAGEMENT
The pace of the economic re-opening and job recovery will also depend on the ability of high contact professions to adopt more constrained interactions as consumers hold back.
Social Distancing and Economic Dislocation
The Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia estimates that there are fifteen professions that are most at risk to COVID-19 dislocation. Approximately 24 million U.S. workers, or 15%, are in this group.
15 largest economically at risk U.S. operations
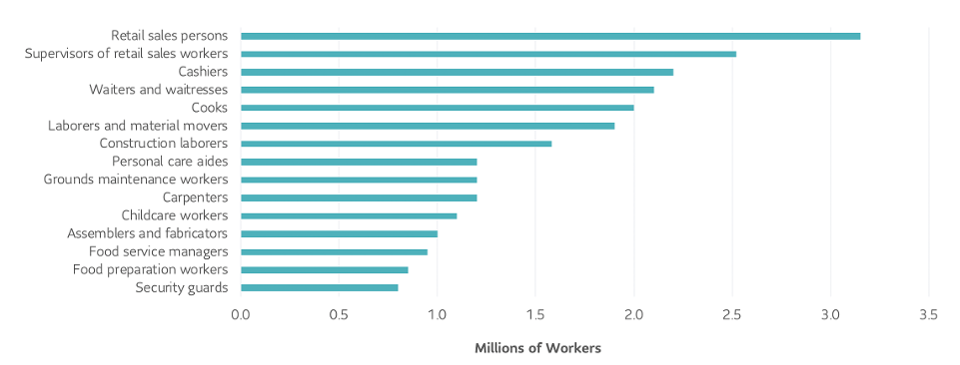
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia (COVID 19: Which Workers Will Be Most Impact by Keith Wardrip and Anna Tranfaglia, April 2020) using data from American Community Survey, 0*Net, BLS Occupational Employment Statistics
15 largest economically at-risk US occupations SLC MANAGEMENT
Many of these professions are in retail, restaurant, food and personal care. Retail will likely shift more of its activity online and restaurants will need to reduce capacity by adding buffer zones and cutting back seating, to installing more curbside pickup options. Some personal care service shops may struggle until vaccines are massively distributed.
Some of these jobs will adapt but up to one third could be dislocated. That could add 5% to structural employment, which on top of a typical frictional / minimal unemployment level of 3.5%, and other fallout, could easily push unemployment levels towards a stubborn 10% well into next year.
Back in 2008, it took almost two years to drag the unemployment rate down from 10% to 9% even as the economy improved. As the crisis continued, companies looked to do more with reduced headcounts. In today’s world, absent a vaccine, companies and individuals may remain cautious as they grapple with recurring threats of virus interruptions.
When Will GDP Growth Pick-Up?
The initial consensus was this virus surge would be an intense but short-lived crisis that would unleash a V-shaped recovery in the second half of the year. That now seems optimistic. The latest growth projections by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) suggest that the world’s output will decrease by 3% in 2020.
Again, the experience from the financial crisis may be instructive. Shock tends to amplify risk aversion for companies and households. Both increased their cash buffers after the Great Financial Crisis in 2008 – 2009 and remained cautious until there was ample evidence the economy was improving. This time is unlikely to be different.
GDP trend leading up to Current Crisis and before & after Financial Crisis
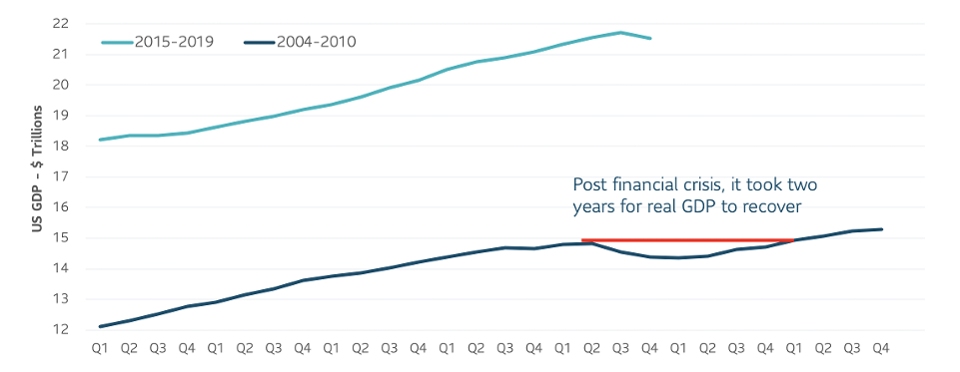
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis
GDP trend leading up to current crisis and before & after financial crisis SLC MANAGEMENT
This article first appeared in Forbes. This material contains opinions of the author, but not necessarily those of Sun Life or its subsidiaries and/or affiliates.